-
 Mail us
Mail usinfo@myhealthhospitals.com
-
 Toll Free
Toll Free+91 9111674111
- Book Appointment
Gi & Laparoscopic
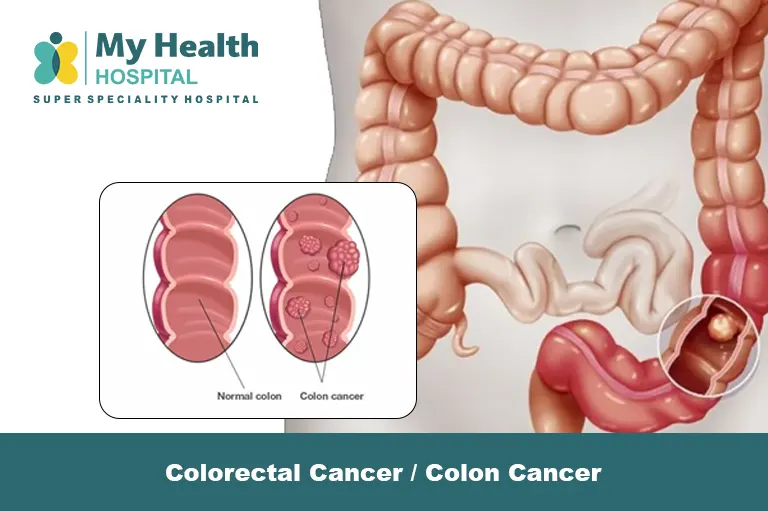
Colorectal cancer, often referred to as colon cancer, originates in the colon or rectum, which are essential parts of the digestive system. This condition typically begins as small, benign clumps of cells called polyps, which can develop into cancer over time if not addressed.
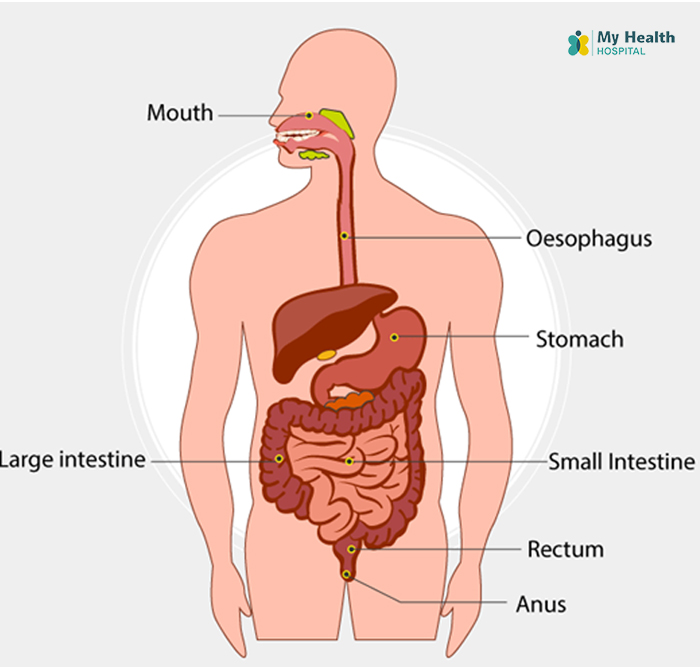
The colon is a long, muscular tube responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from food, while the rectum stores waste before it's excreted. Together, they play a crucial role in digestion.
Cancer in the colon occurs when cells grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system. If left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body.
Having a family history of colorectal cancer increases your likelihood of developing the disease. Certain inherited conditions, like Lynch syndrome, also heighten the risk.
Mutations in genes like APC, KRAS, or TP53 can trigger abnormal cell growth in the colon.
A diet high in red and processed meats but low in fiber may contribute to colorectal cancer.
A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk by affecting overall metabolism and gut health.
Excessive alcohol intake and smoking are known carcinogens that can amplify your risk.
Certain medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, as well as aging, are significant risk factors.
This gold-standard procedure allows for direct visualization and removal of polyps.
Non-invasive tests like fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) detect hidden blood in the stool.
CT scans or MRI can help determine the extent of cancer spread.
A tissue sample is analyzed under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
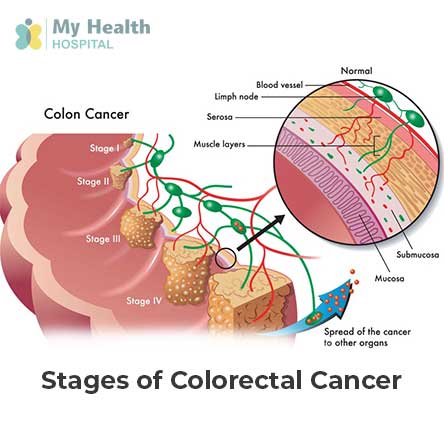
Colorectal cancer is classified into different stages based on the extent of its spread. The stages are typically denoted from 0 to IV:
Colorectal cancer can be categorized into different types based on the specific cells where the cancer begins. The main types include:
Colon cancer treatment often includes surgery to remove the cancer. Depending on the cancer's location and stage, additional treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be recommended. Your healthcare team will also take into account your overall health and personal preferences when developing a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Removing cancerous tissue is often the first line of treatment.
Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or stop their growth.
High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
These treatments focus on specific proteins or genes that fuel cancer growth.
Boosts the immune system to recognize and fight cancer cells.
My Health Hospitals, recognized as one of the leading healthcare institutions in Hyderabad, is dedicated to providing exceptional care for patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer. With state-of-the-art technology, highly qualified medical professionals, and a patient-centric approach, My Health Hospitals ensures comprehensive and personalized care at every stage.
Blood in stool, changes in bowel habits, and unexplained weight loss are common early signs.
Adults over 50 or younger individuals with risk factors should discuss screening schedules with their doctor.
Yes, a family history or genetic mutations can increase the risk.
Absolutely. A diet rich in fiber and low in red meats can help.
Survival rates depend on the stage at diagnosis, with early detection significantly improving outcomes.
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the ENQUIRY form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly
+91 9111674111Visit any of our My Health Hospitals branches for advanced medical care and expert consultations.
H.No 15-24-212, MIG-212, Rd Number 1, K P H B Phase 1, Kukatpally, Hyderabad, Telangana 500072
H.No:-12-5-30, WhiteHouse, Moula Ali Rd, South Lalaguda, Tarnaka, Secunderabad, Telangana 500017