-
 Mail us
Mail usinfo@myhealthhospitals.com
-
 Toll Free
Toll Free+91 9111674111
- Book Appointment
Urology
Kidney stones form when minerals and salts in your urine combine to create hard crystals. Normally, these crystals pass through the urine without any problems. However, when there is insufficient urine volume, the substances become concentrated, leading to crystallization and the formation of stones that may be difficult to pass.
Kidney Stone Surgery Cost in Hyderabad

The stone-forming substances are:
Most of the kidney stones which are small in size (<4 mm ) usually pass in urine along the urinary tract without any symptoms . When the size of the stone is larger (>4mm ) they usually obstruct along their passage and cause symptoms like severe loin/back pain , vomitings , fever which is primarily due to swelling of kidney proximal to the obstructed stone . These stones will not pass along the urine and require surgical removal using Lasers either open or endoscopically depending on the location and size of the stone .
Many kidney stone treatment options are available depending on the stone location and size which are as the following – Kidney stones(PCNL/RIRS/ESWL-laser kidney stone treatment) and Ureteric Stones(laser URSL/laser ureteric stone removal) and for Bladder or urethral stones(CLT- cysto lithotripsy -laser).
Kidney stones, medically known as nephrolithiasis, are mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys. Common symptoms include intense pain in the back and abdomen, blood in the urine, and discomfort during urination. Factors such as dehydration, dietary habits, and genetic predisposition can lead to their development. Treatment options vary from medications and dietary changes to surgical procedures like laser removal. For those seeking the best kidney stone treatment in Hyderabad, early detection and recognition of symptoms, such as pain location and type, are crucial. Preventive measures, including a kidney stone prevention diet and proper hydration, are essential. Consulting a specialist in kidney stone management is advisable for personalized treatment plans that ensure effective and timely care.
Kidney stones develop due to various factors that lead to the accumulation of minerals and salts in the kidneys. Understanding the causes can help in prevention and management.
Not drinking enough water results in concentrated urine, which increases the chances of mineral crystallization and stone formation. Staying hydrated is essential to flush out excess minerals.
A diet high in sodium (salt), animal protein, and sugar can disrupt the urine’s mineral balance, making it easier for kidney stones to form. Processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages should be consumed in moderation.
Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, alters urine composition, increasing the risk of kidney stones. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help prevent stone formation.
Certain health conditions can contribute to kidney stone development, including:
Overuse of Vitamin C, calcium-based antacids, certain laxatives, and dietary supplements can raise the risk of kidney stones by increasing mineral concentrations in the urine.
Kidney stones can cause various symptoms, including:
If you experience severe pain or any of these symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention.

Blood tests: These may include a complete blood count (CBC) to check for infection and serum creatinine to assess kidney function. Other tests can indicate high levels of calcium or uric acid in the blood.
Complete urine analysis (CUE): This helps detect urinary tract infections secondary to stones. A 24-hour urine collection test can reveal excessive excretion of stone-forming minerals like calcium, oxalate, uric acid, or phosphate.
Imaging: High-speed or dual-energy computerized tomography (CT) of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (CT-KUB) can detect even small stones with accurate size and location. Abdominal X-rays may miss tiny kidney stones and cannot detect all types of stones. Ultrasound is another noninvasive and rapid imaging technique, but it is primarily useful for kidney stones.
These diagnostic methods help identify the presence, size, and composition of kidney stones, guiding appropriate treatment.

The treatment of kidney stones varies based on their size and location. Here are the options:
Observation: Smaller kidney stones (<4mm) may pass through your urinary system when you urinate without needing treatment.
Medications: Your urologist may prescribe medications to manage symptoms, such as pain relievers like paracetamol or IV narcotics for severe pain. Antiemetics like ondansetron can help with nausea and vomiting. Medications like tamsulosin or nifedipine may be prescribed to relax your ureter and help the stones pass more easily.
Surgery: If your doctor determines that you need treatment based on the size and location of the stones, surgical options include:
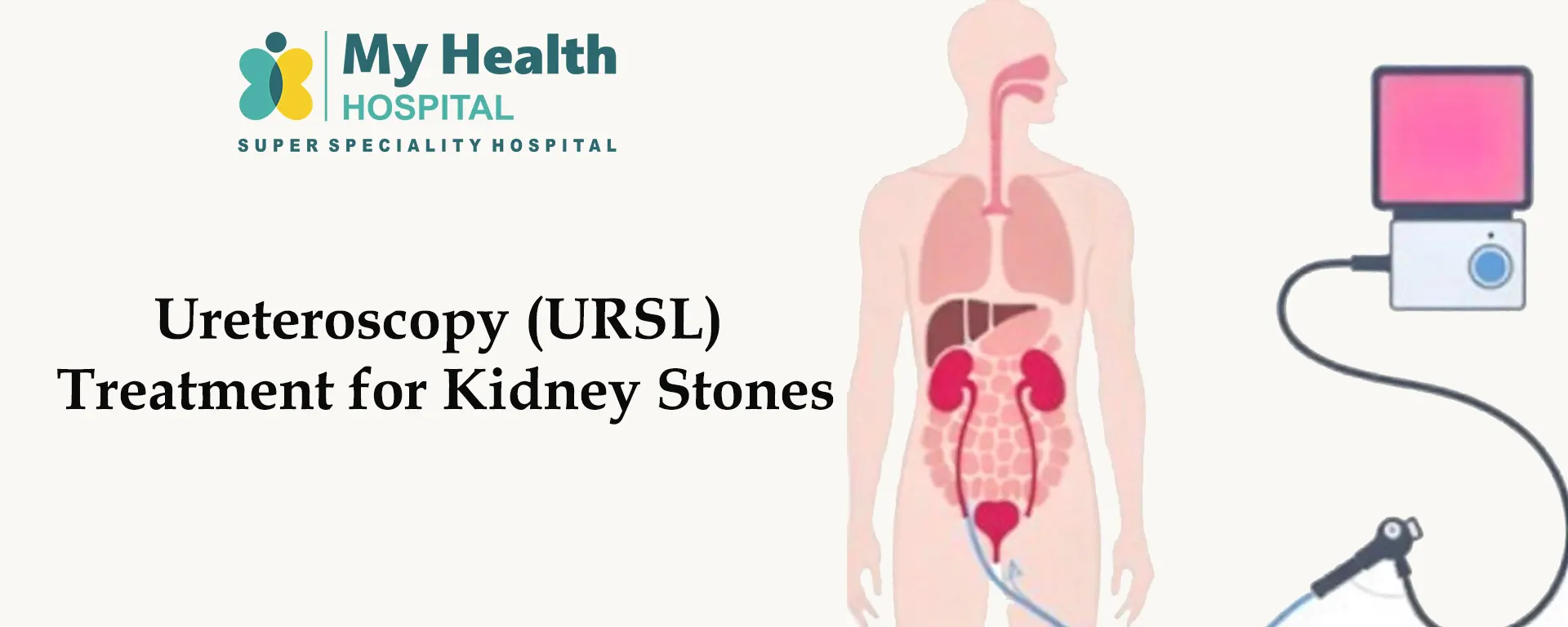
Ureteroscopy (URSL) is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat kidney and ureteral stones. It is commonly performed when stones are too large to pass naturally or are causing severe pain and urinary obstruction.
✅ Minimally invasive – No incisions required.
✅ Quick recovery – Most patients resume daily activities in a few days.
✅ Effective for ureteral stones – High success rate in stone removal.
URSL is a safe and effective treatment option for kidney stones, ensuring faster relief and preventing complications. If you have symptoms of kidney stones, consult a urologist for evaluation.
Shockwave Lithotripsy (ESWL) is a non-invasive procedure used to break kidney and ureteral stones into smaller fragments, allowing them to pass naturally through urine. It is one of the most common treatments for kidney stones, especially for stones that are moderate in size (4mm–20mm).

✅ Mon-invasive – No incisions or surgery required./
✅ Qick recovery – Most patients resume daily activities within a day.
✅ Efective for moderate-sized stones – High success rate for breaking kidney stones.
Shockwave Lithotripsy (ESWL) is a safe and effective kidney stone treatment that offers fast relief with minimal downtime. If you have kidney stones, consult a urologist to determine if ESWL is the right option for you.
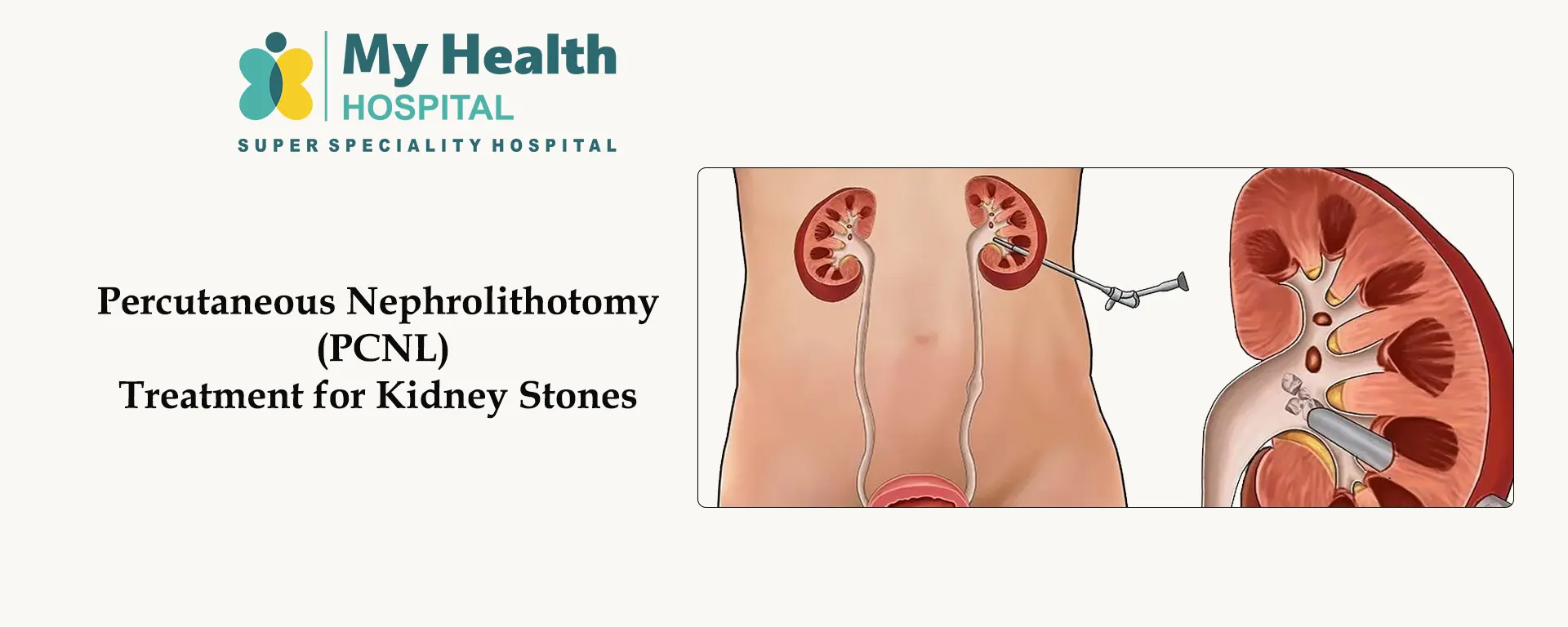
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove large or complex kidney stones that cannot pass naturally or be treated with other methods like ESWL or URSL.
✅ Higher success rate – Effective for large and hard-to-remove stones.
✅ Minimally invasive – Smaller incision compared to open surgery.
✅ Quick stone removal – Unlike ESWL, stones are directly removed, not just broken.
PCNL is the gold standard for treating large kidney stones, providing effective removal with minimal complications. If you have large kidney stones, consult a urologist to determine if PCNL is the right choice for you.
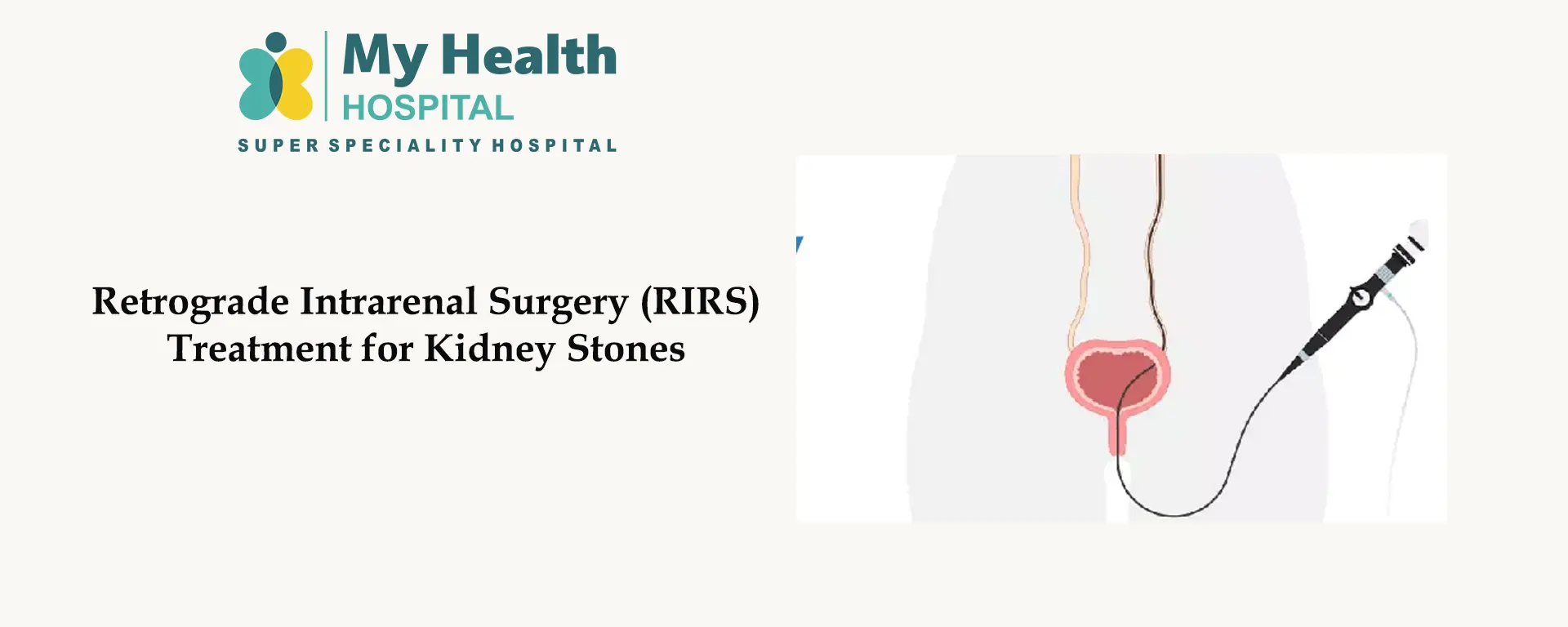
Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS) is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure used to treat kidney stones located in the kidney and upper ureter. It is performed using a flexible ureteroscope and laser technology to break the stones into tiny fragments, which are then passed naturally through urine..
✅ No incisions – Performed through natural urinary pathways.
✅ Quick recovery – Most patients resume normal activities in a few days.
✅ Safe and effective – Ideal for kidney stones in difficult locations.
RIRS is a highly advanced, safe, and effective kidney stone treatment that offers fast relief with minimal downtime. If you have kidney stones, consult a urologist to determine if RIRS is the right choice for you.
Kidney stones can be painful and debilitating, but you can take steps to prevent them. Follow these tips to reduce your risk:
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your urine diluted and prevent the formation of stones.
Eat a balanced diet: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet, and limit foods high in oxalates, such as spinach and nuts.
Monitor your salt intake: Too much salt can increase calcium in your urine, which can lead to stone formation. Limit your salt intake.
Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can increase your risk of developing kidney stones. Aim for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Limit animal protein: Diets high in animal proteins, such as meat and eggs, can increase your risk of kidney stones. Try to limit your intake.
By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing kidney stones and enjoy better kidney health.
Learn More About Kidney StonesUrologists / urology doctors / kidney specialists specialize in diagnosis and treatment kidney stones. you will be explained by the urologist after relavent investigations regarding the size and location of stone and safe and best treatment possible based on the medical condition of the patient.
if you hav a dull aching pain in the back which is persistant and present over some time get it evaluated for presence of kidney stones. or if you experience severe back pain on one side radiating to front with associated burnining micturition /vomitings – you might have a possibility of having a obstructed urteric stone – meet your doctor immeditly.
Some of the possible complications of untreated kidney stones include –
Yes, kidney stones are often associated with nausea, vomiting, and pain in the lower back.
URSL cost - Ureteroscopic liyhotripsy (Ureteric stones) – 60000 - 80,000/- RIRS cost- Retrograde intra renal; surgery ( kidney stones <1 cm )- 90000 to 1.05000 PCNL cost-percutaneous nephrolithotomy (kidney stones >1 cm) - 80000 - 1,20000
My Health Hospitals in Kukatpally, Hyderabad, is one of the best hospitals for kidney stone treatment, offering advanced procedures like URSL, RIRS, ESWL, and PCNL with experienced urologists.
1. stay hydrated
2. have low intake of vegetables rich in oxalates(tomato/spinach)
3. avod high animal protein intake
4. donot neglect any symptoms related to kidney stone
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the ENQUIRY form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly
+91 9111674111